California General Election November 6, 2018
Official Voter Information Guide
PROP
6
ELIMINATES CERTAIN ROAD REPAIR AND TRANSPORTATION FUNDING. REQUIRES CERTAIN FUEL TAXES AND VEHICLE FEES BE APPROVED BY THE ELECTORATE. INITIATIVE CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT.
ANALYSIS BY THE LEGISLATIVE ANALYST
BACKGROUND
APPROVAL OF STATE TAXES
Legislative Requirements. Under the State Constitution, the Legislature can only pass a new tax or increase an existing tax with a two-thirds vote. (The Legislature can pass most other types of laws with a simple majority.) Some state charges referred to as fees (such as vehicle license fees) fall under the constitutional definition of a tax.
Voter Approval Requirements. The Legislature does not need to get voter approval for new or increased taxes that it passes. The voters—through the initiative process—can pass new taxes or increase existing taxes without the Legislature's involvement.
STATE FUEL AND VEHICLE TAXES
Fuel Taxes. The state charges excise taxes on gasoline and diesel fuel. These taxes are set on a per-gallon basis. The state also charges sales taxes on gasoline and diesel fuel. These taxes are set as a percent of the price of the fuel. The State Constitution generally requires that the revenues from these fuel taxes be spent on highways, roads, and transit.
Vehicle Taxes. State law requires vehicle owners to pay two specific taxes for the privilege of operating a vehicle on public highways. These are (1) vehicle license fees and (2) recently enacted transportation improvement fees, both of which are based on a vehicle's value. The State Constitution requires that the transportation improvement fee revenues be spent on highways, roads, and transit.
TRANSPORTATION FUNDING IN CALIFORNIA
Transportation funding in California currently is estimated to total $35 billion. Of this amount, $16 billion comes from local sources, $12 billion from state sources, and $7 billion from federal sources. Local funding mainly comes from sales taxes, transit fares, and city and county general funds, while federal funding mainly comes from federal fuel taxes. State funding mainly comes from state fuel and vehicle taxes. State funding has increased by about three-quarters over the last two years mainly due to recent legislation.
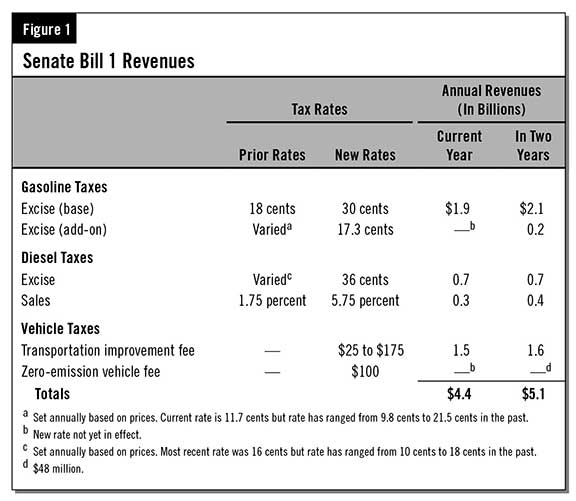
Recent State Transportation Funding Legislation. In 2017, the Legislature enacted Senate Bill (SB) 1 to increase annual state funding for transportation through various fuel and vehicle taxes (shown in Figure 1). Specifically, SB 1 increased the base gasoline excise tax (by 12 cents per gallon) and the diesel sales tax (by 4 percent). It also set fixed rates on a second (add-on) gasoline excise tax and the diesel excise tax, both of which previously could change each year based on fuel prices. Further, SB 1 created the transportation improvement fee (which ranges from $25 to $175 per year) and a fee specifically for zero-emission vehicles (set at $100 per year for model years 2020 and later). It also provides for inflation adjustments in the future. This fiscal year, the state expects the taxes to raise $4.4 billion. Two years from now, when all the taxes are in effect and the inflation adjustments have started, the state expects the taxes to raise $5.1 billion. The State Constitution requires that nearly all of these new revenues be spent on transportation purposes. Senate Bill 1 dedicates about two-thirds of the revenues to highway and road repairs, with the remainder going to other programs (such as for mass transit).
PROPOSAL
Requires Legislature to Get Voter Approval for Fuel and Vehicle Taxes. Proposition 6 amends the State Constitution to require the Legislature to get voter approval for new or increased taxes on the sale, storage, use, or consumption of gasoline or diesel fuel, as well as for taxes paid for the privilege of operating a vehicle on public highways. Thus, the Legislature would need voter approval for such taxes as gasoline and diesel excise and sales taxes, vehicle license fees, and transportation improvement fees.
Eliminates Recently Enacted Fuel and Vehicle Taxes. Proposition 6 also eliminates any such fuel and vehicle taxes passed by the Legislature after January 1, 2017 and up to the date that Proposition 6 takes effect in December. This would eliminate the increased fuel taxes and the transportation improvement fees enacted by SB 1.
FISCAL EFFECTS
Eliminates Tax Revenues From SB 1. In the current fiscal year, Proposition 6 would reduce SB 1 tax revenues from $4.4 billion to $2 billion—a $2.4 billion decrease. (The $2 billion in remaining revenues would be from taxes collected prior to Proposition 6 taking effect in December.) Two years from now, the revenue reduction would total $5.1 billion annually. The funding reductions would mainly affect highway and road maintenance and repair programs, as well as transit programs.
Makes Passage of Specified Fuel and Vehicle Taxes More Difficult. Proposition 6 would make it more difficult to enact specified fuel and vehicle taxes because voters also would have to approve them. As a result, there could be less revenue than otherwise would be the case. Any reduction in revenues is unknown, as it would depend on future actions by the Legislature and voters.
Visit https://www.sos.ca.gov/campaign-lobbying/cal-access-resources/measure-contributions/2018-ballot-measure-contribution-totals/ for a list of committees primarily formed to support or oppose this measure. Visit http://www.fppc.ca.gov/transparency/top-contributors/nov-18-gen.html to access the committee's top 10 contributors.
If you desire a copy of the full text of the state measure, please call the Secretary of State at (800) 345-VOTE (8683) or you can email vigfeedback@sos.ca.gov and a copy will be mailed at no cost to you.
 Back to the Top
Back to the Top