Official Voter Information Guide
[an error occurred while processing this directive]PROP
30
PROVIDES FUNDING FOR PROGRAMS TO REDUCE AIR POLLUTION AND PREVENT WILDFIRES BY INCREASING TAX ON PERSONAL INCOME OVER $2 MILLION. INITIATIVE STATUTE.
ANALYSIS BY THE LEGISLATIVE ANALYST
BACKGROUND
California Personal Income Taxes. The state collects a tax on personal income earned within the state. Last year, the personal income tax raised over $130 billion in revenue. Most of the revenue helps pay for education, prisons, health care, and other public services.
Zero-Emission Vehicle Programs. The state has goals to limit greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change, such as carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels. To help meet these goals, the state has programs that promote zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs)—or vehicles that do not release pollution from the tailpipe. Examples of ZEVs include electric cars and hydrogen fuel cell cars. The state requires ride-sharing companies (such as Uber and Lyft) to use an increasing number of ZEVs for their services. The state also gives some funding to help households, businesses, and governmental agencies buy new ZEVs and install fueling infrastructure, such as charging stations for electric cars.
Wildfire Response and Prevention Programs. The state has the main responsibility for wildfire response activities—commonly known as firefighting—on about one-third of California’s land area. (The federal government and local agencies have the main responsibility for wildfire response everywhere else in California.) Wildfire response activities help limit the spread of large wildfires and stop them from damaging communities and harming residents. The state also runs wildfire prevention programs to reduce the chances that wildfires will start and to limit the damage they cause when they do occur. Some examples of wildfire prevention activities include removing trees from overgrown forests and clearing dead plants that are likely to catch on fire in areas near buildings.
PROPOSAL
CREATES A NEW TAX ON HIGH-INCOME TAXPAYERS
Beginning January 2023, Proposition 30 requires taxpayers with incomes above $2 million each year (annually) to pay an additional tax of 1.75 percent on the share of their income above $2 million. This additional tax would end by January 2043. The tax could end several years earlier if California is able to drop its statewide greenhouse gas emissions below certain levels before then.
USES REVENUE TO EXPAND ZEV PROGRAMS AND WILDFIRE ACTIVITIES
Proposition 30 requires that the revenue from the new tax go to increasing funding for ZEV programs and wildfire activities, as shown in Figure 1. The money would go to several state agencies to manage the programs and activities.
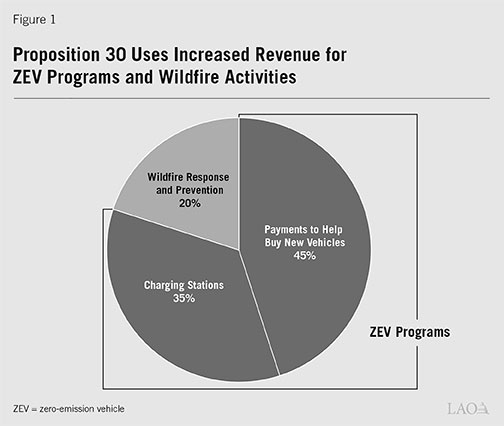
ZEV Programs (80 Percent). About 80 percent of the total revenue is for two ZEV program categories:
- Payments to Help Buy New Vehicles. Most of this money must be used to help households, businesses, and governments pay for part of the cost of new passenger ZEVs (such as cars, vans, and pick-up trucks). The rest of the money would be available for other programs. These include payments to businesses and governments to help buy large ZEVs (such as trucks and buses) and programs that encourage less driving and improve local air quality.
- Charging Stations. This money would be used to install and operate ZEV charging and fueling stations at places such as apartment buildings, single-family homes, and public locations.
For each category above, at least half of the money must be spent on projects that benefit people who live in or near heavily polluted and/or low-income communities. The rest of the money could be spent on projects anywhere in the state.
Wildfire Response and Prevention Activities (20 Percent). About 20 percent of total revenue must be spent on wildfire response and prevention activities. In general, the state would have to prioritize spending to hire, train, and retain state firefighters. The rest of the money could be used for other wildfire response and prevention activities.
FISCAL EFFECTS
Increased State Tax Revenues From New Tax for ZEV Programs and Wildfire Activities. The new tax on high-income taxpayers typically would raise $3.5 billion to $5 billion annually, growing over time. This range reflects the changes in the incomes of high-income taxpayers. Their incomes often change greatly due to changes in the economy and stock market. Based on the spending requirements in Proposition 30, this funding would support:
- ZEV Programs. The proposition would increase state funding for ZEVs by $2.8 billion to $4 billion annually. The state typically spends hundreds of millions of dollars annually on ZEV programs and also recently committed to spending about $10 billion over a five-year period on these programs.
- Wildfire Response and Prevention Activities. The proposition would increase state funding for wildfire response and prevention activities by $700 million to $1 billion annually. The state typically spends about $2 billion to $4 billion annually on wildfire activities, mostly on firefighting.
Potential State and Local Effects From Increased ZEV Spending. The additional funding for ZEV programs under Proposition 30 could impact the number of ZEVs, as well as gasoline- or diesel-powered vehicles, being driven in California. However, the actual effect the proposition would have is uncertain for a variety of reasons. Most notably, while this analysis was being written, the state was considering requiring that car companies sell an increasing share of ZEVs in future years until 2035 when they would only be able to sell ZEVs. (The state was scheduled to decide on this requirement by August 2022.) This requirement is sometimes called a "ZEV mandate." The proposition’s potential transportation-related fiscal effects on state and local governments depend on whether or not the ZEV mandate is approved.
- If the state approves the ZEV mandate, then the additional funding from the proposition to help buy new ZEVs would not have much effect on the total number of ZEVs driven in California. This is because the ZEV mandate would already require a significant increase in the number of ZEV sales, even without the additional spending. Instead, the proposition’s main effect would be to shift who pays for the ZEVs. That is, more costs would be covered by revenue from the new tax on high-income taxpayers instead of by vehicle sellers and/or buyers. This would not have much effect on state and local finances.
- If the state does not approve the ZEV mandate, then the funding from the proposition to help buy new ZEVs would increase the number of ZEVs—and decrease the number of gasoline- or diesel-powered vehicles—driven in California. As a result, the amount of gasoline being used would be less. Over the long term, this change could have several different fiscal effects on state and local governments, including lower gasoline tax revenues that are used for transportation projects, higher revenues from electricity taxes, and other effects related to less air pollution. The net fiscal effect of these changes are uncertain, but likely minor compared to the hundreds of billions of dollars state and local governments spend annually on all activities.
Potential Decreased State and Local Costs for Wildfire Response and Recovery. Proposition 30 could somewhat decrease state and local government costs related to firefighting, clean-up, and recovery if the additional funding for wildfire activities ends up reducing the severity of future wildfires. However, any cost reductions would depend on (1) which specific wildfire activities end up being funded, (2) how effectively these activities reduce wildfire severity, and (3) the severity of wildfires that would have otherwise taken place in any specific year. All of these factors are uncertain, which makes the size of the potential fiscal effects on state and local governments unclear.
Decreased State Revenue for Other Activities. Some taxpayers probably would take steps to reduce the amount of income taxes they owe. This would reduce existing state revenues used to pay for activities not funded by Proposition 30. The degree to which this would happen and how much revenue the state might lose as a result is unknown.
Potential Reductions to Other State Programs to Comply With State Spending Limit. With some exceptions, such as responding to emergencies and building infrastructure, the California Constitution limits how much the state can spend. In recent years, state spending has reached this limit. Some of the spending required by Proposition 30—likely an amount ranging from about $1.5 billion to $3 billion annually—would count toward this limit. As a result, when state spending is at the limit, the proposition would require the state to reduce an equal amount of spending from other programs to "make room" for the new required spending on ZEV programs and wildfire activities.
Visit https://www.sos.ca.gov/campaign-lobbying/cal-access-resources/measure-contributions/2022-ballot-measure-contribution-totals for a list of committees primarily formed to support or oppose this measure.
Visit https://www.fppc.ca.gov/transparency/top-contributors.html to access the committee's top 10 contributors.
 Back to the Top
Back to the Top